SAE J995 TECHNICAL DATA
Order SAE J995 Grade 2 Nuts Order SAE J995 Grade 5 Nuts Order SAE J995 Grade 8 Nuts
The SAE J995 specification is formally known as Mechanical and Material Requirements for Steel Nuts. The SAE J995 Standard covers the mechanical and material requirements for three grades of steel nuts ranging in size from ¼ to 1-1/2 inches with dimensions adhering to SAE J428 or ASME B18.18. The nuts in the standard are typically used in automotive and related engineering applications.
SAE J995 Grades & Identification Markings
There are three grades of nuts within the SAE J995 Standard. The grades are 2, 5, and 8. As the grade number increases, the tensile strength of the nut increases. For each of the three grades, there are three acceptable styles of grade marking. Style A of marking is applicable to all sizes of nuts. Style B is applicable to hex nuts sized 5/8 inches or larger. Style C is applicable to nuts that are fabricated by cutting from a hex bar.
Grades & Identification Markings
| Chemical Composition Requirements 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUT Grade | C Max | Mn Min | P Max | S Max | Grade Identification Marking |
| 2 | 0.55 | - | 0.12 2 | 0.15 3 | 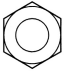 |
| 5 | 0.55 | 0.3 | 0.05 4,5 | 0.15 3,5 | 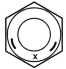 |
| 8 | 0.55 | 0.3 | 0.04 | 0.15 6 | 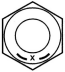 |
1. All values are for ladle analysis (percent by weight) and subject to standard variations for check analysis as given in SAE J409.
2. Resulfurized and rephosphorized material is not subject to rejection based on check analysis for sulfur.
3. If agreed between purchaser and producer, sulfur content may be 0.23 maximum.
4. Phosphorus content may be 0.13 maximum for acid bessemer steel only.
5. If agreed between purchaser and producer, sulfur content may be 0.35 maximum
and phosphorus content may be 0.12 maximum provided that manganese content is 0.70 minimum.
6. If agreed between purchaser and producer, sulfur content may be 0.33 maximum provided that manganese content is 1.35 minimum.
SAE J995 Mechanical Properties
SAE J995 mechanical requirements specify the proof load the nut must be able to withstand according to the nut size, thread series, and nut type. The mechanical properties also include requirements for tensile stress areas and nut hardness limits.
PROOF LOAD REQUIREMENTS
| Nut Grade | 2 | 5 | 8 | |||||
| Nut Size | 1/4 thru 1 1/2 | 1/4 thru 1 1/2 | 1/4 thru 1 | 1/4 thru 1 | Over 1 thru 1 1/2 | Over 1 thru 1 1/2 | 1/4 thru 1 1/2 | 1/4 thru 1 1/2 |
| Thread Series | UNC and 8UN | UNF, 12 UN and Finer | UNC and 8UN | UNF, 12 UN and Finer | UNC and 8UN | UNF, 12UN and Finer | UNC and 8UN | UNF, 12UN and Finer |
| Nut Type | Proof Load Stress, psi1 | Proof Load Stress, psi1 | Proof Load Stress, psi1 | Proof Load Stress, psi1 | Proof Load Stress, psi1 | Proof Load Stress, psi1 | Proof Load Stress, psi1 | Proof Load Stress, psi1 |
| Hex | 90000 | 80000 | 120000 | 109000 | 105000 | 94000 | 150000 | 150000 |
| Hex Flange | 90000 | 80000 | 120000 | 109000 | 105000 | 94000 | 150000 | 150000 |
| Hex Jam2 | 54000 | 48000 | 72000 | 65000 | 63000 | 57000 | 90000 | 90000 |
| Heavy Hex Jam2 | 54000 | 48000 | 72000 | 65000 | 63000 | 57000 | 90000 | 90000 |
| Hex Slotted2 | 71000 | 65000 | 96000 | 87000 | 84000 | 75000 | 120000 | 120000 |
| Heavy Hex2 | 100000 | 90000 | 133000 | 120000 | 116000 | 105000 | 165000 | 150000 |
| Hex Thick2 | 100000 | 90000 | 133000 | 120000 | 116000 | 105000 | 165000 | 150000 |
| Hex Thick Slotted2 | 79000 | 71000 | 105000 | 96000 | 92000 | 84000 | 132000 | 120000 |
| Hex High2 | 100000 | 90000 | 133000 | 120000 | 116000 | 105000 | 165000 | 150000 |
| Hex High Slotted2 | 79000 | 71000 | 105000 | 96000 | 92000 | 84000 | 132000 | 120000 |
| Square | 90000 | 80000 | 105000 | 96000 | 92000 | 84000 | 132000 | 120000 |
| Heavy Square | 79000 | 71000 | 105000 | 96000 | 92000 | 84000 | 132000 | 120000 |
1. The proof load in pounds for nuts is computed by multiplying the proof load stress, in psi (lbf/in2 ), for the nut grade, size, thread series, and type, as shown in Table 2, and tensile stress area in square inches (in2 ), for the applicable
size and thread series shown in Table 3. (For tabulated values see Appendix A.) To convert the inch based pounds per square inch (psi) values above to metric Megapascal (MPa) units, multiply the above values by .00689.
2. Proof load stress values for hex jam, heavy hex jam, hex slotted, heavy hex, hex thick, heavy hex slotted, and hex thick slotted nuts are based on the requirement for hex nuts. Primarily, each value is derived from the ratio
of the minimum thickness of the product involved to the minimum thickness of similar hex or square machine screw nuts and hex nuts (see B18.2.2) of the same size
TENSILE STRESS AREA
| Coarse Thread Series UNC Nominal Size and Threads Per Inch | Coarse Thread Series UNC Tensile Stress Area, sq in. | Fine Thread Series UNF Nominal Size and Threads Per Inch | Fine Thread Series UNF Tensile Stress Area, sq in. | 8-Thread Series 8 UN Nominal Size and Threads Per Inch | 8-Thread Series 8 UN Tensile Stress Area, sq in. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4 - 20 | 0.0318 | 1/4 - 28 | 0.0364 | - | - |
| 5/16 -18 | 0.0524 | 5/16 -24 | 0.0580 | - | - |
| 3/8 - 16 | 0.0775 | 3/8 - 24 | 0.0878 | - | - |
| 7/16 - 14 | 0.1063 | 7/16 - 20 | 0.1187 | - | - |
| 1/2 - 13 | 0.1419 | 1/2 - 20 | 0.1599 | - | - |
| 9/16 - 12 | 0.182 | 9/16 - 18 | 0.203 | - | - |
| 5/8 - 11 | 0.226 | 5/8 - 18 | 0.256 | - | - |
| 3/4 - 10 | 0.334 | 3/4 - 16 | 0.373 | - | - |
| 7/8 - 9 | 0.462 | 7/8 - 14 | 0.509 | - | - |
| 1 - 8 | 0.606 | 1 - 12 | 0.663 | 1 - 8 | 0.606 |
| 1-1/8 - 7 | 0.763 | 1-1/8 - 12 | 0.856 | 1-1/8 - 8 | 0.790 |
| 1-1/4 - 7 | 0.763 | 1-1/8 - 12 | 0.856 | 1-1/8 - 8 | 0.790 |
| 1-1/4 - 7 | 0.969 | 1-1/4 - 12 | 1.073 | 1-1/4 - 8 | 1.000 |
| 1-3/8 - 6 | 1.155 | 1-3/8 - 12 | 1.315 | 1-3/8 - 8 | 1.233 |
| 1-1/2 - 6 | 1.405 | 1-1/2 - 12 | 1.581 | 1-1/2 - 8 | 1.492 |
HARDNESS
| Nut Grade | Nominal Nut Size | Hardness |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1/4 thru 1-1/2 | 32 HRC max |
| 5 | 1/4 thru 1-1/2 | 32 HRC max |
| 8 | 1/4 thru 5/8 | 24-34 HRC |
| 8 | Over 5/8 | 26-34 HRC |
| 8 | Over 1 thru 1-1/2 | 26-36 HRC |
SAE J995 Materials & Chemical Properties
The chemical composition requirements outlined by the SAE J995 Specification set the maximum amounts of carbon, phosphorus, and Sulphur as well as the minimum amount of manganese in the composition of the steel used to manufacture the nut.
MATERIALS & CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
| Nut Size | Marking Lines1 Width | Marking Lines1 Length | Marking Lines1 Depth |
| 1/4 and 5/16 | 0.015 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| 3/8 thru 9/16 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| 5/8 thru 7/8 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
| 1 and larger | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
1. For hex flange nuts, lines on the top of the flange may be up to two times the dimensions shown.
